
Input samples can represent historical data with a large number of input parameters and expected output. It frequently occurs when the input file “Sample.csv” has been generated by a legacy system or extracted from an enterprise data repository. Not all data instances in such files correctly represent the business problem for which we want to generate a decision model.
When subject matter experts look at such instances, they quickly notice possible inconsistencies that may mislead Rule Learner. For example, some instances are outliers that should be removed from the samples. Subject matter experts may decide to change some instances and/or to add new ones that better represent the problem. They also may prefer not to mix all samples together but rather split them into different categories by selecting only those instances that satisfy certain criteria.
Rule Learner includes a Rule Trainer that supports such capabilities. It allows a subject matter expert to define business (training) rules that may filter the provided samples to exclude outliers and/or generate different decision models concentrating only on selected issues within large sets of samples with historical data. Rule Trainer acts as a pre-processor of Rule Learner by preparing better source instances for discovering better business rules.
How does Rule Trainer work? As a user, you usually create your own Rule Learner project by copying the project “Template”. Its sub-folder “Learning” along with the file “Samples.csv” already contains the standard file “Learn.xls”. This file is a placeholder for problem-specific training rules that should analyze all Source Instances and produce Filtered Instances. By default, the file “Learn.xls” includes the following decision table “FilterTrainingInstances“:
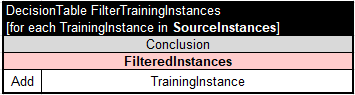
This table unconditionally copies all provided SourceInstances to FilteredInstances without any filtering or modifications. However, you may advance this decision table by adding conditions that will exclude undesirable source instances included in “Samples.csv”.
For example, Rule Learner includes the project “Credits” with 1,000 of sample instances that classify debtors as “good” or “bad” based on different combinations of their attributes. If you open the file “Credits/Learning/Learn.xls” you will see the modified version of the above decision table “FilterTrainingInstances“:

This table iterates over all training instances from the array “SourceInstances” and selects only those instances for which “Age >= 30” and “Foreign Worker Is yes“. Such instances will be copied to the array “FilteredInstances”.
Similarly, you may add any conditions to the proper decision table inside your project to filter source instances before they will be used by ML algorithms to generate classification rules. The excluded instances still will be included in the automatically generated tests and can be used to verify the generated rules against unknown instances.
This described mechanism allows domain experts to incorporate their knowledge into Rule Learner by presenting it in a form of problem-specific training rules.
Thus, Rule Trainer provides a user with greater control over the generated decision model to ensure accuracy and relevance of business rules.


